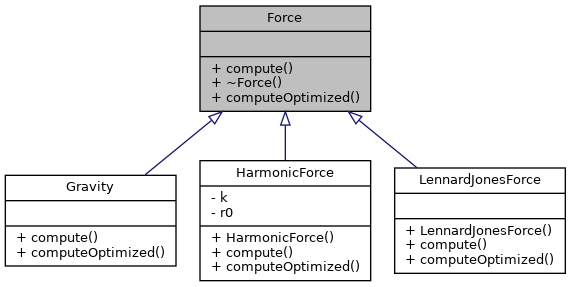
Interface representing the force that the source exerts on the target. More...
#include <Force.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual std::array< double, 3 > | compute (Particle &target, Particle &source)=0 |
| Actual computation of the force occurring. More... | |
| virtual | ~Force ()=default |
| virtual std::array< double, 3 > | computeOptimized (Particle &target, Particle &source, std::array< double, 3 > &difference, double distance)=0 |
| We needed this to integrate our optimization in our code to prevent breaking the inheritance hierachy. Will be removed, when we integrated the optimization properly. More... | |
Detailed Description
Interface representing the force that the source exerts on the target.
This interface provides a generalization of the force that might occur between two particles. There are different types of forces which may all implement this interface.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ ~Force()
|
virtualdefault |
Member Function Documentation
◆ compute()
Actual computation of the force occurring.
- Parameters
-
target Particle on which the force acts. source Particle which exerts the force on the target.
- Returns
- 3 dimensional force vector.
This method may be implemented by any child of this class according to the type of force it represents.
Implemented in LennardJonesForce, HarmonicForce, and Gravity.
◆ computeOptimized()
|
pure virtual |
We needed this to integrate our optimization in our code to prevent breaking the inheritance hierachy. Will be removed, when we integrated the optimization properly.
Implemented in LennardJonesForce, HarmonicForce, and Gravity.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- /home/runner/work/MolSim/MolSim/src/moleculeSimulator/forceCalculation/Force.h